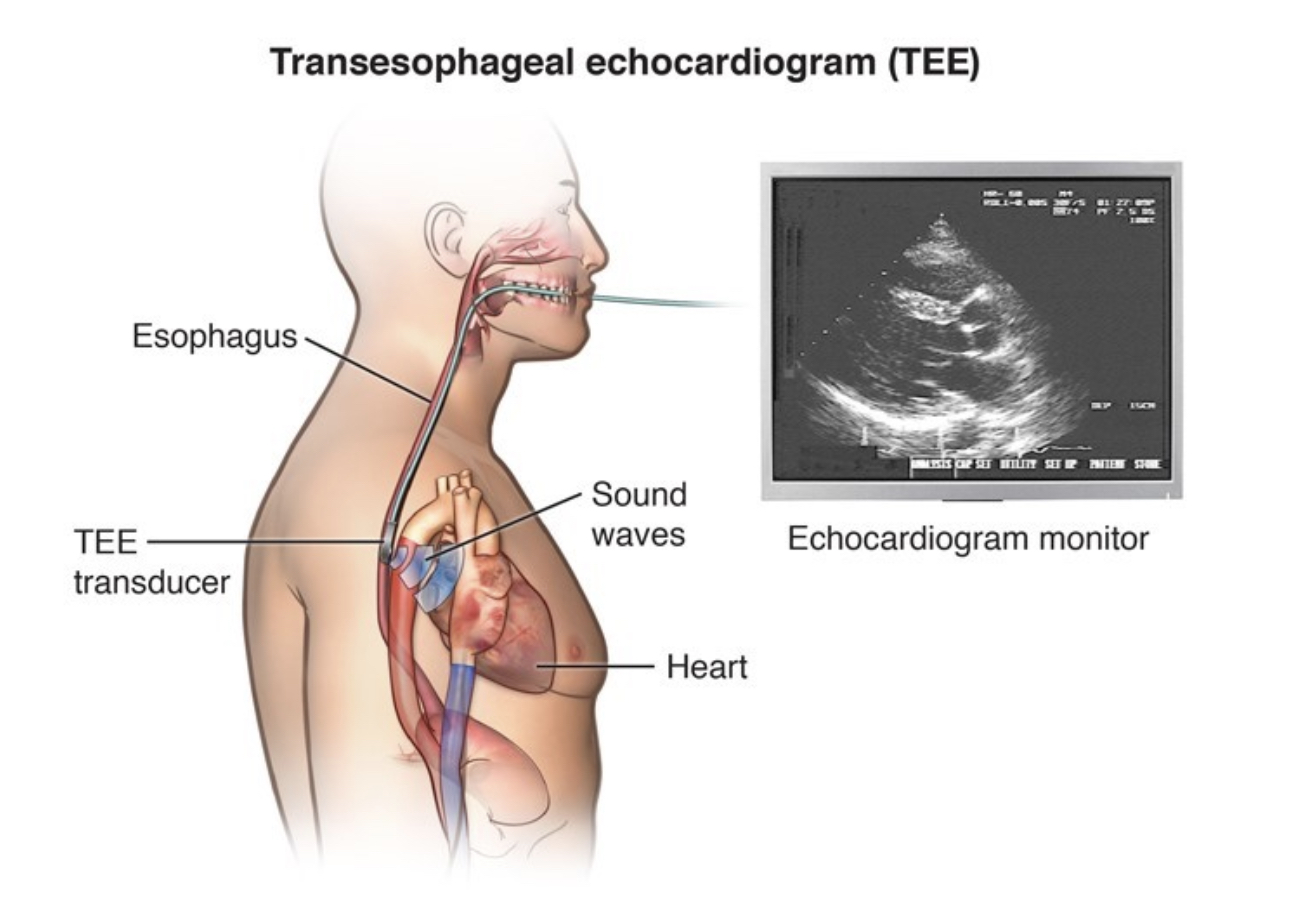
A transesophageal echocardiogram (TEE) uses echocardiography to assess the structure and function of the heart. During the procedure, a transducer sends out ultrasonic sound waves.
When the transducer is placed at certain locations and angles, the ultrasonic sound waves move through the skin and other body tissues to the heart tissues, where the waves bounce or “echo” off of the heart structures. The transducer picks up the reflected waves and sends them to a computer.
The computer displays the echoes as images of the heart walls and valves.